Chapter 10.1-10.3 – Photosynthesis: light and light reactions
OBJECTIVE: Explain how photosynthesis converts light energy to chemical energy and the role of chloroplasts in these processes.
- In general, what is the purpose of photosynthesis?
- Write the summary equation of photosynthesis from memory.
- Indicate above which reactant becomes reduced and which becomes oxidized.
- How does the summary equation of photosynthesis compare to the summary equation of cellular respiration?
- Fill in the missing reactants and products into the diagram below.
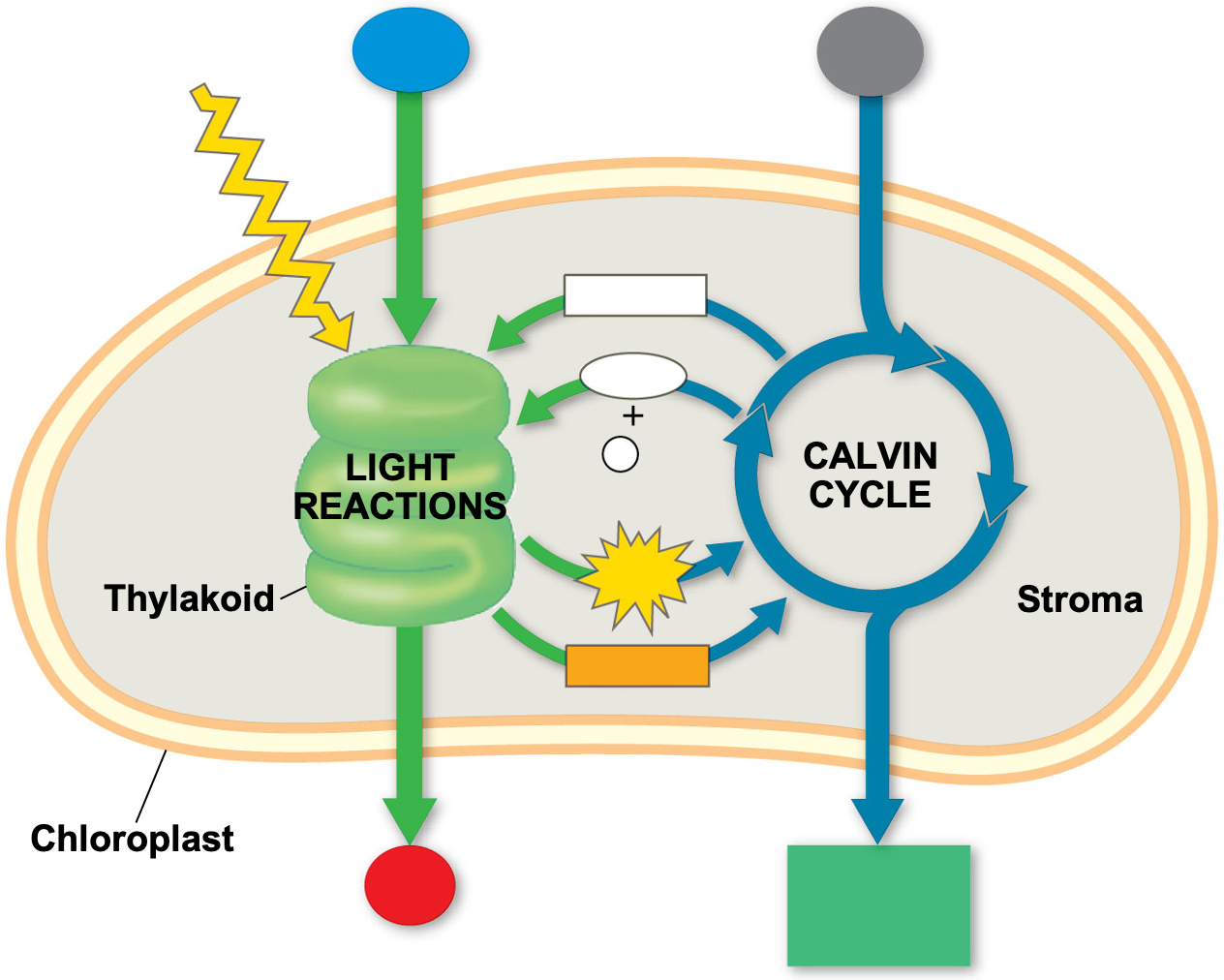
- What is the MAIN function of the light reactions?
- What is the MAIN function of the Calvin Cycle?
-
Use Figure 10.2 and the summary equation of photosynthesis to complete the table below for the two stages (components) of photosynthesis.
Stage location Input molecules Output Molecules Function 1. 2. -
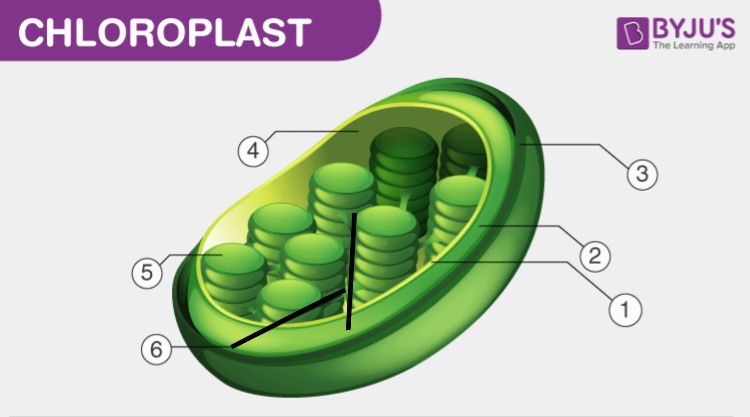
Label the Outer membrane, inner membrane, Stroma, Grana, and Thylakoid in the diagram of a chloroplast below.
OBJECTIVE: Describe the role of different pigments in photosynthesis and plant protection.
- In general, what do pigment molecules do?
-
Refer to Figure 10.5 and 10.7. Name three different pigment types found in chloroplasts and list the colors of light each of these pigments absorbs and transmits.
Pigment Colors Absorbed Colors Transmitted Main function - Look at the table you just filled in. Why isn’t green light as useful for photosynthesis as other colors?
-
Look at Fig 10.8. Are pigments proteins?
OBJECTIVE: Describe the sequence of events that occurs after an electron is excited by a photon.
- What happens to electrons when the pigment absorbs light?
- List 4 things that can happen to after an electron in chlorophyll is excited (from lecture, not all of these are in your book)
- Describe the physical (spacial) arrangement of the light harvesting complex and the reaction center complex within the photosystem. What does the light harvesting complex accomplish with this arrangement?
- Describe what happens to an electron once energy is passed to chlorophyll a in the reaction center? What molecule captures the electron?
- From which molecule does P680 replace its lost electron?
- The electron transport chain an electron moves through after being excited by PSII is responsible for producing what useful molecule? How does it do this? Compare with cellular respiration.
- What important, high-energy molecule is produced by the electron transport chain following Photosystem I?
- In summary, what 2 molecules are produced by the electron transport chains?
- In what membrane are the photosystems and electron transport chains embedded?
- On which side of this membrane are ATP and NADPH produced?
- What is the difference between ‘linear’ and ‘cyclic’ electron flow?
- What does cyclic electron flow accomplish?